Rotating dressing tools execute an additional rotational movement (Fig. 6-4). If the dressing tool has the negative profile of the grinding wheel, only a radial feed motion is necessary. Dressing rollers that do not engage across the entire wheel width require however a lateral feed.
Common rotating diamond tools for dressing grinding wheels are:
• diamond profile rollers,
• diamond form rollers and
• diamond cup wheels (Fig. 6-5).
Diamond cup wheels are preferred for dressing grinding wheels in batch production. Their area of application is however limited to straight profiles. For dressing grinding wheels with non-linear shapes, diamond profile rollers and diamond form rollers are more advantageous.
Diamond profile rollers bear the negative profile of the grinding wheel. By a radial infeed frd the profile of the diamond roller is formed on the grinding wheel. Diamond profile rollers make possible a high level of reproduction precision in short amounts of dressing time. Due to their minimal flexibility, they are predominantly used in mass production. Diamond form rollers are, on the other hand, more flexible. The desired contour is produced on the grinding wheel under NC control. In this way, varying grinding wheel profiles can be created. The disadvantages are the larger mechanical effort and the longer dressing times of these dressing tools.
For gear grinding, special dressing tools are employed, such as diamond dressing gears or diamond dressing discs (Fig. 6-6). For dressing grinding wheels for continuous gear grinding, sets of dressing discs and diamond profile rollers are the most often used tools [LIER03].
|
form roller |
dressing discs |
profile roller |
gear wheel |
Diamond dressing rollers can be produced in the positive method (the direct method) or the negative method (the reverse method) [MINK99, YEGE89]. In the case of the positive method, the diamonds are directly applied onto a profiled body. The grain density is average, the grain distribution is statistical and the geometrical surface shape is determined by the variation in diamond grit size.
The negative method works with lost moulds which have the reverse profile of the dressing roller (Fig. 6-7). Hand-placed or randomset diamonds on the profile surface are bonded with each other galvanically or by means of infiltration methods and united with a base body. Since the diamonds are lined up with the specified profile of the negative mould, the amount of accuracy obtainable is preset by the negative mould.
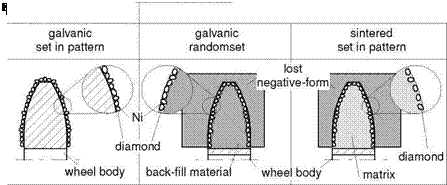
The selection of diamond specification, grit size and diamond pattern, considerably influences the result of the dressing [BRIN95, ELEM03, KLOC87, LIER02, ODON76]. For example, a profile roller can be supplied in the shoulder region with a cruder diamond grit size in lower concentration than the face, so that the dressing process produces a higher effective grinding wheel surface roughness in the shoulder region [TYRO03]. The danger of thermal stress can thus be avoided for shoulder grinding [KLOC87].
Of the greatest practical importance in the reverse (negative) method are diamond rollers with the highest possible packing density. The diamond grit sizes applicable are essentially determined by the concave profile areas of the negative mould.
