2.2.1 Chemistry, Types and Characteristics of Silicon
Silicon carbide, also known as carborundum and SiC, is used as abrasive material in its hexagonal form, a-SiC (Fig. 2.10) [MALK08, p. 24]. It is composed of 70.05 wt % Si and 29.95 wt% C [LIET08]. Each C atom is surrounded by four Si atoms and vice versa. The proportion of covalent atom bonds to ionic atom bonds is 90-10 % [MULL01, p. 25]. Silicon carbide occurs in two modifications: cubic P-SiC and aSiC (mostly hexagonal and rhombohedral).
![Подпись: Density 3.21 g/cm3 [LIET08] Hardness Knoop 24 - 26 GPa [MULL01]* Fracture toughness 3.1 MPa m1/2 [MULL01]* Thermal stability Up to 1500 oC [MULL01]* Thermal conductivity 100 W/ m K [ROWE09] ‘after 3M, GE, Norton, Treibacher](/img/3149/image025_0.gif) |
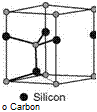 |
Fig. 2.10 Basic properties of а-silicon carbide, picture source [PRES08]
• Green silicon carbide has higher purity and is mainly used for precision grinding [TYRO03b].
• Black silicon carbide has higher toughness and is used for rough grinding operations [TYRO03b].
The chemical composition is shown in Table 2.2.
