2.1.1 Chemistry, Types and Characteristics of Corundum
 |
![Подпись: Density 3.97 g/cm3 [MULL01]* Hardness Knoop 21 - 24 GPa [MULL01]* Fracture toughness 2.2 MPa m1/2 (3.8 MPa m1/2 for sol- gel-corundum) [KLOC02] Melting temperature 2,027 oC [SALM07] Thermal stability Up to 1750 oC [MULL01] Thermal conductivity 35 W/ m K [ROWE09] *after 3M, GE, Norton, Treibacher](/img/3149/image007_0.gif) |
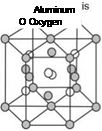
Corundum is crystalline aluminum oxide, Al2O3, and also known as alumina. Al2O3 is also the active element in the natural abrasive material emery [LEWI76, p. 9] and in the gemstones sapphire and ruby. Aluminum oxide occurs in at least five modifications, a-Al2O3, P-Al2O3, y-Al2O3, 5-Al2O3, and e-Al2O3. The technologically most important modification is the rhombohedral crystalline a-Al2O3, being the basis for corundum (Fig. 2.2). The proportion of covalent atom bonds to
ionic atom bonds is 40-60 % [MULL01, p. 25]. The cubic form y-Al2O3 (clay, German “Tonerde”) is the basis for vitrified bonds and other ceramic products.
Industry applies several corundum types with different chemical composition and manufacturing routes:
• Molten or fused corundum, such as
— Brown corundum (also known as brown fused alumina, BFA, semi-friable corundum, regular corundum),
— White corundum (also known as pure white alumina),
— Pink corundum,
— Ruby corundum (also known as red alumina),
— Zirconium corundum (also known as alumina zirconia),
— Mono crystalline corundum (also known as single crystal alumina),
— Micro crystalline corundum,
— Hollow sphere corundum (also known as bubble alumina)
• Sintered corundum
• Sol-Gel corundum
Table 2.1 gives the chemical composition of several types of molten corundum.
