 |
 |
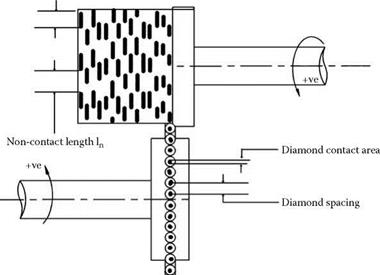
The rotary diamond differs from a stationary tool in that it is not cutting a continuous thread in the wheel, but, consisting as it does of a ring of exposed diamond points, it is cutting a series of
|
Wheel/grit contact length ld
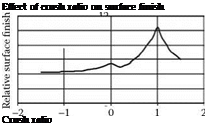
FIGURE 7.18 Wheel surface appearance generated by a single diamond ring rotary truer traversing with an overlap factor of one. |
“divets” out of the grinding wheel. For a truing disc with a single ring of diamonds, the overlap factor, Ud, is dependent on the diamond spacing in order to ensure complete cleanup of the wheel face (Figure 7.18).
Also, for a well-defined spacing of diamonds, if a stone is missing or misplaced it can set up repetitive patterns on the face of the wheel, which transfers to the ground surface. The truer designs to be discussed below, therefore, fall into two categories: those with a series of accurately spaced diamonds akin to a rotary blade dresser, and truers with a totally random distribution of diamonds in a metal matrix akin to rotary grit tools.
Disc dressers are the rotary equivalent of the blade tool. They contain a ring of diamond held in a sintered or brazed matrix, and lapped to a precise form. Traditionally, the diamonds were high — quality long natural stones, but are now being replaced in many cases by polycrystalline diamond (PCD) and more recently chemical vapor deposition materials. Companies such as Dr. Kaiser and Precidia (Saint-Gobain Abrasives) have specialized in their manufacture. Typical roll tolerances and a range of forms as given by Dr. Kaiser are shown below (Figure 7.19 and Figure 7.20).
The use of this type of roll is reserved for the highest precision operations with tight finish requirements <0.4 Ra. The rolls are expensive but can hold radii as small as 200 pm for >10° included angle and 100 pm for >30° included angle. Larger radii are held to ±10 pm allowing a precise value to be entered into a CNC control to generate an accurate wheel profile.