7.3.1 Introduction
Perhaps the most widely sought after, but as yet unavailable, stationary tool is the one that can dress high-performance vitrified cubic boron nitride (CBN) wheels. The problem is that singlepoint and needle diamonds wear much too quickly for most superabrasive wheels at the speeds the wheels must operate. Grit tools leave the wheels too dull and create too much pressure. There are a couple of exceptions, however: dressing small and/or low concentration wheels.
7.3.2 Jig Grinding
Jig grinding, such as on Moore jig grinders, uses a range of CBN and diamond wheels. The process has a relatively low stock-removal requirement because most applications are still performed dry and the wheels must be mounted on long quills to get deep into, for example, mold cavities. The wheel spindle is usually pneumatically driven and can be slowed to a few hundred rpm for dressing, making the wheel act extremely soft. Using small diameter, high-porosity wheels, the author has even had acceptable life with single-point diamond tools dressing dry (although this would not be the optimum process, it can do a job).
7.3.3 Toolroom Grinding
The other area is again in the toolroom targeted at grinding steels such as D2, A2, and M2 on low-power reciprocating surface grinders. Several wheel makers have produced products such as Memox from Noritake, CBLite from Norton (Saint-Gobain Abrasives), and Vitrazon TR from Universal (Saint-Gobain Abrasives) that are low-concentration vitrified CBN wheels with relatively high porosity. At low stock-removal rates typical of a surface grind operation (Q’w < 1 mm3/mm/s), they can still achieve a G-ratio of 500 to 1,000. The attraction of this type of wheel is that it can remove material at a rate as fast or faster than that of a conventional wheel, since in most cases the process is limited more by spindle power and machine stiffness, while an unskilled operator can set a grinder up to remove a given depth of stock without having to compensate repeatedly for wheel wear. This type of wheel has been dressed with single points, but more often grit tools and needle diamond blade tools. The following recommendations are found in the trade literature: [1]
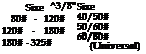 |
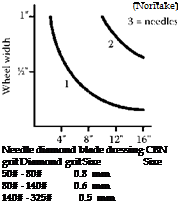 |
FIGURE 7.15 Grit tool and needle blade tool recommendations for dressing low concentration vitrified cubic boron nitride wheels.
