The quality and price of the diamond abrasive grain grade is governed both by the consistency of shape and the level of entrapped solvent in the stones. Since most of the blockiest abrasive is used in metal bonds processed at high temperatures, the differential thermal expansion of metal inclusions in the diamond can lead to reduced strength or even fracture. Other applications require weaker phenolic or polyimide resin bonds processed at much lower temperatures and use more angular, less thermally stable diamonds. Grit manufacturers, therefore, characterize their full range of diamond grades by room temperature toughness (TI), thermal toughness after heating at, for example, 1,000°C (TTI), and shape (blocky, sharp, or mosaic). Included in the midrange, sharp grades are both crushed natural as well as synthetic materials.
3.4.5 Diamond Coatings
Diamond coatings are common. One range includes thick layers or claddings of electroplated nickel, electroless Ni-P, copper, or silver at up to 60%wt. The coatings behave as heat sinks, while increasing bond strength and keeping abrasive fragments from escaping. Electroplated nickel, for example, produces a spiky surface that provides an excellent anchor for phenolic bonds when grinding wet. Copper and silver bonds are used more for dry grinding, especially with polyimide bonds, where the higher thermal conductivity outweighs the lower strength of the coating [Jakobuss 1999]. Attention should be paid to wheel Material Data Safety Sheets (MSDS) to confirm chemical composition to ensure any coating used does not present a contaminant problem. For example, silver contamination may be a problem in grinding of titanium alloys.
Coatings can also be applied at the micron level either as a wetting agent or as a passive layer to reduce diamond reactivity with the particular bond. Titanium is coated on diamonds used in nickel-, cobalt-, or iron-based bonds to limit graphitization of the diamond while wetting the
|
|
||
|
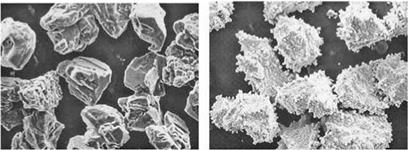
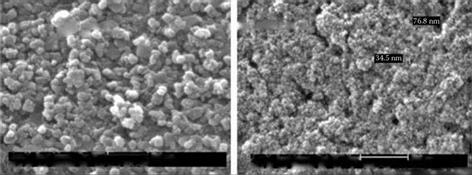
diamond surface. Chromium is coated on diamonds used in bronze — or WC-based bonds to enhance chemical bonding and reactivity of the diamond and bond constituents.
Finally, for electroplated bonds, the diamonds are acid etched to remove any surface nodules of metal solvent that would distort the plating electrical potential on the wheel surface leading to uneven nickel plating or even nodule formation. It also creates a slightly rougher surface to aid mechanical bonding.
