Aircraft grade aluminum alloys are used as hub materials for some high-speed vitrified CBN. The obvious attraction is the lower density relative to steel. Various grades are available with tensile strengths of 120 to 140 kpsi. However, they have higher thermal expansion and appear to give more size and stability problems.
4.6.8 Junker Bayonet Style Mounts
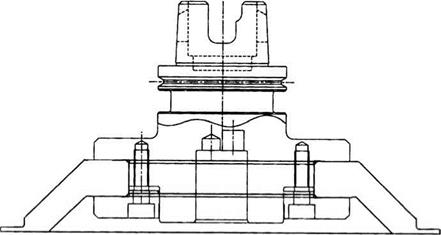
Other methods have been developed to compensate for bore expansion. Erwin Junker Maschinen — fabrik developed a patented bayonet-style cam and follower three-point type mount. Various forms of the design are shown in Figure 4.20. The first consists of three roller bearings inserted into the bore, the second is the later, more common, version consisting of a hardened steel ring insert with three premolded raised areas as detailed. The design assures <1.25 pm runout repeatability at speeds up to 140 m/s [Junker n. d. 1992].
4.6.9 HSK Hollow Taper Mount
Another method is the incorporation of the increasingly popular HSK tool holder shank. The HSK system was developed in the late 1980s at Aachen T. H., Germany as a hollow tapered shaft capable of handling high-speed machining. It became a shank standard in 1993 with the issuance in Germany of DIN 69893 for the hollow 1:10 taper shank together with DIN 69063 for the spindle receiver.
This system has seen a rapid growth, especially in Europe, as a replacement to the various 7:24 steep taper shanks known as the CAT or V-flange taper in the United States (ASME-B5.10-1994), the SK taper in Germany (DIN69871), and the BT taper in Japan (JISC-B-6339/BTJISC). These tapers previously dominated the CNC milling industry.
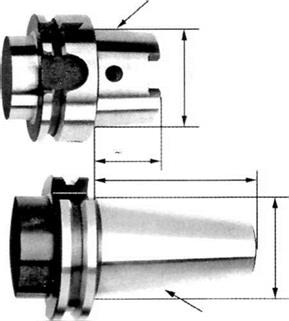
The HSK system actually consists of a family of shank sizes from 25 to 160-mm flange diameter and designs from A thru F, of which the HSK-A is the most common for grinding applications with flange diameters from 80 to 125 mm. Muller-Held [1998] reported that the HSK system could limit maximum position deviations to 0.3 pm compared with 2 pm for an SK taper. Lewis [1996] reported it was 3 times more accurate in the X and Y planes and 400 times better in the Z axis. Bending stiffness was 7 times better, while the short length of the taper allowed faster tool change times. The important detail, however, for this discussion is the fact that the design has a hollow taper that expands under centrifugal load to aid the maintenance of contact. However, Aoyama and
 (CAT, SK, BT)
(CAT, SK, BT)
FIGURE 4.21 Comparison of the HSK mount with earlier CAT and other taper systems.
Inasaki [2001] reported that radial stiffness reduces with increased rotational speed but is still far superior to any other taper mounting system.
The HSK wheel mount system has been widely adopted for hybrid grinding/metal cutting machines. Regular 1A1 style-plated wheels have been routinely run at up to 140 m/s on HSK taper arbors. At least one research machine has been built using a one-piece hub design incorporating HSK
Wheel mount surface
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
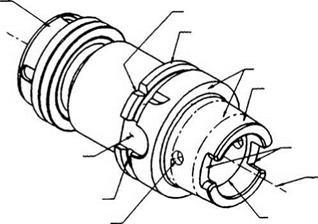
Ledge for automatic drawbar clamping
|
FIGURE 4.23 Plated CBN groove grinding wheel mounted on HSK adaptor. |
mounting for use up to 250 m/s. Currently the primary hesitation in broader adoption of this technique is the cost, availability, and delivery due to the limited number of capable high-precision manufacturing sources.