Bearing preload needs to be carefully controlled and understood. Insufficient preload leads to low stiffness while excessive preload leads to higher temperature rise and even seizure. As rotational speed increases several factors cause an increase in preload: [4]
Schematic drawing showing general arrangement of lubrication system
3/8 Steel tubing


![]()
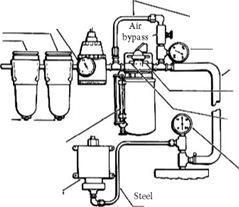 External by-pass line added to all spindle lubricators when air flow exceeds 6 SCFM. External by-pass not required for air flow less than 6 SCFM.
External by-pass line added to all spindle lubricators when air flow exceeds 6 SCFM. External by-pass not required for air flow less than 6 SCFM.
Use internal air by-pass for air flows less than 6 SCFM.
Gage no. 2 secondary pressure 1/2* tubing
Controls internal by-pass air. Set closed when using external by-pass. Adjust for correct pressures per instructions when no external by-pass is used.
Controls rate of oil feed through sight feed dome. Set for 60-65 drops per min. Note: Locations of drop rate and internal by-pass adjusting screws are reversed on. lubricators designed for right-to-left air flow. Gage no. 3
or plastic tubing Spindle pressfure gage (gage. to read
15 psi for all spindles)
In addition to affecting preload, thermal effects cause expansion of the spindle arbor leading to axial positional error. To minimize preload effects, several options are available to the machine tool builder as follows.
15.12.4 Use of Ceramic Balls for High-Speed Spindles
The first option is the use of hybrid ceramic (silicon nitride) ball bearings. Ceramic balls have a lower density than steel to reduce centrifugal forces; they have lower friction coefficient to reduce frictional heating and lower thermal expansion to minimize the effects of heating. Ceramic is also chemically inert and allows the oil-film to work better and for longer. In many cases, the attraction of ceramics balls is to allow grease-packed lubrication at higher DN values. Hybrid ceramic bearings can be rated for 0.8 to 1.4 m DN when grease packed, or to 2 to 3 m DN with oil-mist lubrication [Nakamura 1996, Aronson 1994, 1996].
15.12.5 Liquid Cooled High-Speed Spindles
The second option is to liquid cool the spindle by pumping oil through the housing and even injecting cooled oil into the bearings either as a metered oil-air mixture based on monitoring spindle characteristics (i. e., with greater control than a standard oil-mist system) or as a flood jet of oil. The oil-air approach can play a major role in extracting heat from the whole spindle as well as maintaining a positive pressure to the bearings to prevent contamination.
