The third group of alloys is cobalt based. These alloys display the best high-temperature corrosion resistance but have the lowest grindability and are the most expensive. They are, therefore, used in just the hottest part of the engine. However, one area where expense is not so important and where strength and corrosion resistance are critical is in the medical industry where wrought and cast cobalt-chromium alloys are becoming common for implants such as knee and hip joints. They are strengthened by solid-solution elements and the presence of carbides, and experience the same problems in grindability as the aerospace industry. Plated CBN and extruded ceramic grain are common for this type of application.
13.4.3 Titanium
Figure 13.7 gives typical values for the relative grindability of many of the material types described above. These numbers are dependent on advances in the various abrasive and wheel bond technology
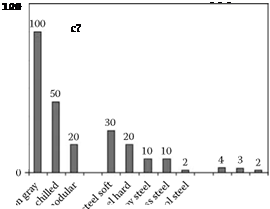 |
FIGURE 13.7 Relative grindability by material type.
and on the type of application. With the growth of CBN technology, the grindability of hard steel and chilled iron has increased significantly. Similarly, recent developments in extruded ceramic grain technology may raise the grindability of nickel — and cobalt-based alloys based on G-ratio and stock removal parameter from those shown. Titanium alloys are also included in Figure 13.7. Titanium is problematic because it is chemically reactive with CBN limiting the application of superabrasives; it is also reactive with alumina. Some success has been reported using plated diamond [Kumar 1990] to grind aerospace-grade titanium alloys, but most applications still use porous SiC wheels. On the other hand, the machinability of titanium remains better than nickel — or cobalt-based alloys based on chip form and surface quality, and in many cases should be considered as a better alternative to grinding.
Badger, J. A. 2003. “Grindability of High-Speed Steel.” Abrasives Mag. Dec-Mar, 16-19.
Kumar, K. V. 1990. “Superabrasive Grinding of Titanium Alloys.” SME Conference Proceedings, Paper MR90-505.
![]()
